Types of Security Concerns
Security concerns are prevalent in various aspects of our lives, ranging from physical security to cybersecurity and beyond. Addressing these concerns is paramount to safeguarding individuals, organizations, and assets from potential harm or loss. In this article, we will delve into the different types of security concerns and explore strategies to mitigate them effectively.
Introduction to Security Concerns
Definition of Security Concerns
Security concerns encompass any potential threat or risk to the safety, integrity, or confidentiality of individuals, organizations, or assets.
Importance of Addressing Security Concerns
Addressing security concerns is crucial as failure to do so can result in significant consequences, including financial loss, reputational damage, and even physical harm.
Physical Security Concerns
Physical security involves measures taken to protect physical assets, premises, and individuals from unauthorized access, theft, vandalism, or harm.
Overview of Physical Security
Physical security measures may include surveillance systems, access control mechanisms, security guards, and perimeter barriers.
Common Physical Security Threats
Common physical security threats include burglary, theft, trespassing, vandalism, and natural disasters such as fires or floods.
Strategies for Mitigating Physical Security Concerns
Mitigating physical security concerns involves implementing robust security protocols, conducting regular risk assessments, and investing in advanced security technologies.
Cybersecurity Concerns
Cybersecurity focuses on safeguarding digital assets, networks, and systems from cyber threats such as malware, phishing, hacking, and data breaches.
Understanding Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity encompasses preventive measures, detection mechanisms, and response strategies to protect against cyber threats.
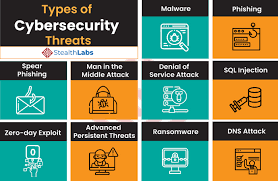
Types of Cybersecurity Threats
Cybersecurity threats include viruses, ransomware, DDoS attacks, social engineering, and insider threats.
Best Practices for Enhancing Cybersecurity
Enhancing cybersecurity involves implementing strong passwords, regularly updating software, encrypting sensitive data, and providing employee training on cybersecurity awareness.
Social Engineering Threats
Social engineering is the practice of coercing someone into disclosing private information or doing activities that jeopardize security.
Definition of Social Engineering
Social engineering tactics exploit human psychology to deceive individuals into divulging sensitive information or performing unauthorized actions.
Examples of Social Engineering Attacks
Examples of social engineering attacks include phishing emails, pretexting phone calls, and impersonation scams.
How to Protect Against Social Engineering Threats
Protecting against social engineering threats requires education, vigilance, and implementing security measures such as multi-factor authentication and security awareness training.
Data Breach Concerns
Unauthorized persons gaining access to private or sensitive data can result in data loss or disclosure, which is known as a data breach.
Explanation of Data Breaches
Data breaches can occur due to various factors, including malware infections, insider threats, weak security controls, or human error.
Causes of Data Breaches
Common causes of data breaches include inadequate security measures, unsecured networks, outdated software, and lack of employee awareness.
Steps to Prevent Data Breaches
Preventing data breaches involves implementing robust cybersecurity protocols, encrypting sensitive data, conducting regular security audits, and establishing incident response plans.
Insider Threats
Insider threats refer to security risks posed by individuals within an organization who misuse their access privileges to compromise security.
Definition of Insider Threats
Insider threats may include malicious insiders seeking to steal data or sabotage systems, as well as inadvertent actions by employees that result in security breaches.
Types of Insider Threats
Types of insider threats include disgruntled employees, negligent insiders, and malicious insiders collaborating with external attackers.
Methods to Mitigate Insider Threats
Mitigating insider threats requires implementing access controls, monitoring employee behavior, conducting background checks, and providing ongoing security training.
Emerging Security Concerns
Emerging security concerns encompass new and evolving threats that pose challenges to traditional security measures.
Overview of Emerging Security Threats
Emerging security threats may include artificial intelligence-driven attacks, Internet of Things vulnerabilities, and geopolitical cyber conflicts.
Examples of Emerging Security Concerns
Examples of emerging security concerns include deepfake technology, quantum computing risks, and supply chain vulnerabilities.
Strategies to Stay Ahead of Emerging Threats
Staying ahead of emerging threats requires proactive risk management, continuous monitoring of security trends, collaboration with cybersecurity experts, and investing in innovative security solutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and addressing various types of security concerns are essential to safeguarding individuals, organizations, and assets in an increasingly interconnected world. By implementing robust security measures, staying informed about emerging threats, and fostering a culture of security awareness, we can mitigate risks and protect against potential harm.
Unique FAQs
- How can individuals enhance their cybersecurity?
- What role does employee training play in mitigating security risks?
- How do businesses recover from a data breach?
- What are the implications of failing to address security concerns?
- How can emerging technologies impact cybersecurity threats?